How to Develop a Blockchain Application: A Beginners Guide
- BLOG
- Blockchain
- October 18, 2025
Blockchain applications are redefining how digital transactions, data exchanges, and trust are handled across industries. Unlike traditional applications that rely on centralized systems, blockchain apps (often called dApps or decentralized applications) are built on distributed ledgers. This architecture ensures transparency, immutability, and enhanced security; features that are increasingly valuable in today’s data-sensitive environment.
From finance to supply chain to healthcare, blockchain adoption is accelerating, not just for cryptocurrency use cases but for solving real-world inefficiencies. As businesses push for innovation and trustless ecosystems, understanding how to develop blockchain applications becomes crucial for developers, startups, CTOs, and entrepreneurs who want to stay ahead of the curve.
This guide is tailored specifically for:
- Developers looking to build secure, scalable, and modern applications using blockchain frameworks
- CTOs planning to integrate decentralized infrastructure within their products
- Startups aiming to launch Web3 products or platforms
- Entrepreneurs exploring blockchain as a business model or competitive differentiator
The potential here is massive. According to NextMSC,
“The global Blockchain Market size was valued at USD 24.20 billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach USD 301.02 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 60.2% from 2025–2030.”
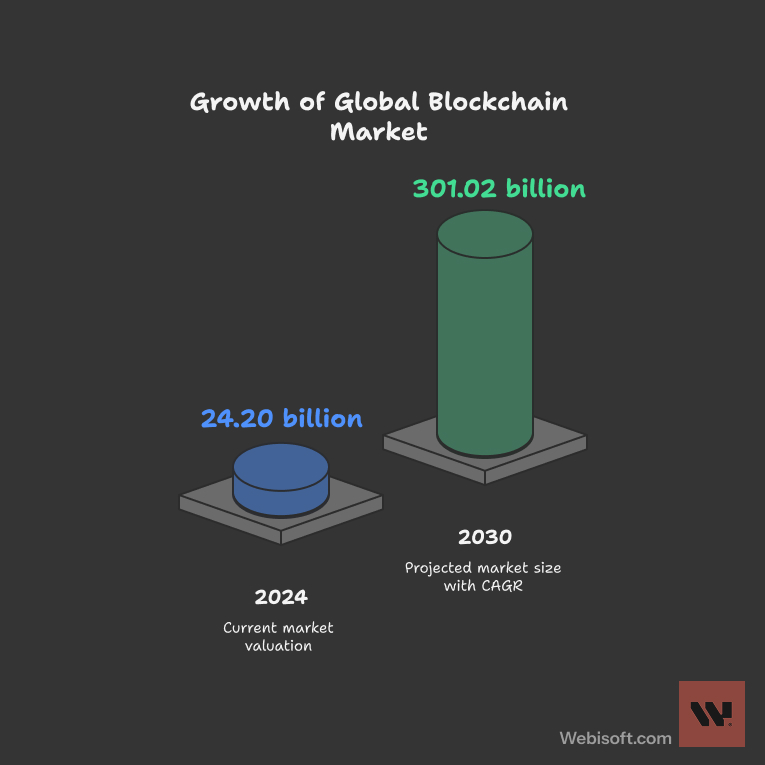
That level of growth signals not just hype, but sustained transformation in how industries operate. And with the rise of Layer 2 solutions, smart contracts, and enterprise adoption, there’s no better time to explore how blockchain apps are designed and deployed.
As Ginni Rometty, former IBM CEO, put it:
“Blockchain will do for trusted transactions what the internet did for information.”
In the sections that follow, we’ll take a practical, step-by-step approach to developing blockchain applications, covering everything from choosing the right platform to ensuring long-term scalability and security.
Contents
- 1 What is a Blockchain Application?
- 2 How Does a Blockchain App Work?
- 3 Popular Use Cases of Blockchain Applications
- 4 Key Benefits of Blockchain App Development for Businesses
- 5 Step-by-Step Guide to Developing a Blockchain Application
- 5.1 Step 1 – Define the Problem and Use Case
- 5.2 Step 2 – Choose the Right Blockchain Type
- 5.3 Step 3 – Select the Best Blockchain Development Platform
- 5.4 Step 4 – Choose the Consensus Mechanism
- 5.5 Step 5 – Design the Architecture
- 5.6 Step 6 – UI/UX Design for Blockchain Apps
- 5.7 Step 7 – Smart Contract Development
- 5.8 Step 8 – Test and Debug Thoroughly
- 5.9 Step 9 – Deployment and Monitoring
- 5.10 Step 10 – Maintenance, Upgrades, and Governance
- 6 Blockchain App Tech Stack: Tools and Frameworks
- 7 Cost of Developing a Blockchain Application
- 8 Common Challenges and How to Solve Them
- 9 Best Practices for Secure and Scalable Blockchain Development
- 10 Future Trends in Blockchain App Development
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 Here are some FAQs we encounter by several of our readers
- 12.1 What are the main types of blockchain networks?
- 12.2 How long does it take to develop a blockchain app?
- 12.3 Can I use traditional programming languages for blockchain apps?
- 12.4 What are the top platforms for launching a dApp?
- 12.5 How do I ensure smart contract security?
- 12.6 What is gas optimization and why is it important?
- 13 Partner with Us
What is a Blockchain Application?
When people hear “blockchain,” their minds often jump straight to Bitcoin or Ethereum. But blockchain technology goes way beyond cryptocurrency. At its core, a blockchain application is any software built to run on a decentralized network, where control isn’t in the hands of a single entity, but distributed across participants.
Instead of relying on a central database, blockchain apps store their data on a shared ledger that multiple nodes verify in real-time. This setup makes tampering extremely difficult, and trust becomes a feature of the system, not a matter of faith in any one organization.
There are three main types of blockchain apps you’ll encounter:
- Public blockchain apps, like those built on Ethereum or Solana, are open to anyone. Anyone can interact with the network or contribute code.
- Private blockchain apps are more controlled and used within organizations or closed groups where access is restricted.
- Consortium blockchain apps sit somewhere in between, they’re governed by a group of organizations rather than a single player.
Compared to traditional apps, blockchain apps introduce some big differences. You don’t just build a backend and hook up a frontend. You’re also working with smart contracts (self-executing code), consensus protocols, and often have to account for things like gas fees, tokenomics, and wallet integration.
Some real-world examples include:
- A crypto wallet app like MetaMask that lets users store and interact with tokens
- An NFT marketplace like OpenSea where ownership of digital assets is recorded immutably
- A decentralized exchange (DEX) like Uniswap that runs entirely via smart contracts, no central broker needed.
How Does a Blockchain App Work?
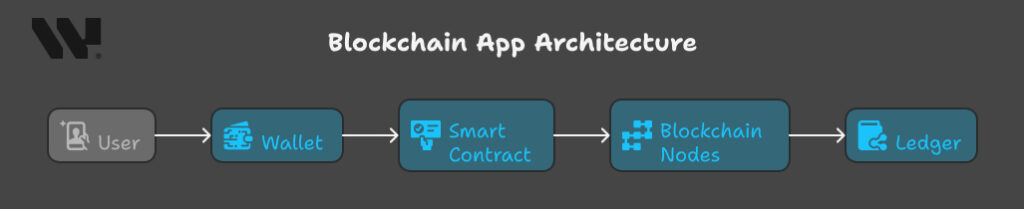
If you’ve built a traditional web app before, you’ll notice that developing a blockchain app changes some foundational assumptions. You’re still dealing with frontend and backend, but the backend is where things get decentralized, immutable, and, well… a little weird at first.
Backend: Where the Blockchain Magic Happens
At the heart of a blockchain app are smart contracts, its a self-executing pieces of code that live on the blockchain. Once deployed, they can’t be altered (unless you design them to be upgradeable). These contracts define the logic of your app, everything from token transfers to NFT minting rules to how voting mechanisms work in a DAO.
Instead of a centralized server, your app interacts with a network of nodes, computers that validate and propagate transactions. Every node maintains a copy of the ledger, and transactions are only accepted once consensus is reached. Depending on the blockchain, consensus might come from Proof of Stake (PoS), Proof of Work (PoW), or more exotic methods like Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
Frontend: Still Familiar
The frontend still looks like any regular web or mobile app, built with React, Vue, or React Native. But instead of calling REST APIs, it connects to smart contracts via Web3 libraries like web3.js or ethers.js, often through browser extensions like MetaMask.
Talking to the Chain
Whether your app is built on Ethereum, Solana, or Hyperledger, the architecture shifts slightly depending on how fast, scalable, or permissioned the chain is. Ethereum is great for DeFi and NFTs, but gas costs can be a pain. Solana offers speed, but has a steeper learning curve with Rust. Hyperledger fits better in enterprise scenarios where control and privacy are crucial.
A Real-World Analogy
Think of it like this:
A traditional app is like Google Docs where all your data sits on Google’s servers.
A blockchain app is more like a shared notebook where every user keeps their own identical, constantly synced copy. You can’t change your page without everyone else seeing and agreeing it’s legit.
Popular Use Cases of Blockchain Applications
When people hear “blockchain,” they still often jump to crypto trading or Bitcoin speculation. Fair, but way too narrow. Blockchain apps are quietly reshaping everything from banking and supply chains to how we vote or even prove ownership of digital art.
Let’s walk through a few use cases I’ve either explored hands-on or closely followed in the field.
Finance & DeFi
This one’s the poster child and for good reason. Decentralized finance (DeFi) apps like Uniswap, Aave, and wallets like MetaMask have completely flipped traditional banking logic. You don’t need a bank account or an ID to lend, borrow, or swap tokens.
A few years ago, it felt like a niche. Now?
“In 2025, approximately 28% of American adults, or about 65 million people, own cryptocurrencies.”
— Security.org
I remember onboarding a friend to Aave in 2021. He went from skeptical to obsessed in about an hour after realizing he could earn interest without asking permission from anyone.
Supply Chain
Supply chain was the first space I saw blockchain make real business sense in. You’re dealing with multiple stakeholders, and trust breaks down constantly. Enter blockchain: tamper-proof provenance tracking.
IBM Food Trust is a standout example, it helps companies like Nestlé and Walmart trace ingredients across every point of the journey.
“In 2025, brands like Nestlé, Walmart, and De Beers are using blockchain to verify the origin of products like food, diamonds, and clothing.”
— LinkedIn Pulse
It’s not just hype, either:
“The global market value of blockchain in the food industry and agriculture sector is projected to reach a valuation of $1.5 billion by 2026.”
— Appinventiv
Healthcare
Patient record access is a mess. I’ve seen clinics emailing unencrypted PDFs. That’s where blockchain comes in not just for storing records, but controlling access with full transparency.
And the investment is catching up:
“The global blockchain in the healthcare market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 63.85% from 2018 to 2025, to reach a value of $5.61 billion by 2025.”
— BIS Research
Real Estate
Smart contracts are streamlining title transfers, escrow, and even rental agreements. I’m watching some early experiments where properties are “tokenized” and split into tradable digital shares. There’s still regulatory friction, but the upside is huge: faster transactions, fewer intermediaries.
Voting & Governance
Estonia ran early blockchain-based elections. It’s still early days, but the vision is clear: verifiable, tamper-proof digital voting. I think it’ll take off once trust in traditional systems erodes further (which… yeah).
Gaming & Metaverse
If you’ve played Axie Infinity or wandered through Decentraland, you’ve already seen blockchain powering in-game economies. I tested a play-to-earn game where my assets were fully tradable NFTs. It felt futuristic but also glitchy and clunky. Still, it’s improving fast.
NFTs & Digital Collectibles
Beyond the art hype, NFTs are solving real problems in digital ownership. Whether it’s certifying a rare in-game skin or authenticating a music file, the potential goes far beyond pixelated monkeys.
Key Benefits of Blockchain App Development for Businesses
Whether you’re running a fintech startup, a logistics platform, or even a healthcare SaaS; blockchain isn’t just “nice to have” anymore. It’s becoming a strategic edge.
When used right, a blockchain application can unlock tangible business value. Here’s how.
Radical Transparency & Immutability
Blockchain records are append-only, once data is written, it can’t be altered or deleted without leaving a trace. That means everyone (partners, auditors, regulators) sees the same version of the truth. No more reconciling messy Excel sheets from three departments.
For sectors like supply chain, finance, and insurance, this clarity can eliminate disputes and speed up decisions.
Security via Decentralization
Unlike centralized databases that can be compromised by a single point of failure, blockchain distributes data across nodes. If one node gets hacked, the network stays intact.
I’ve seen early-stage startups use this architecture to protect sensitive transactions without needing massive cybersecurity budgets.
Cost Reduction Through Smart Automation
Smart contracts are the backbone of blockchain apps as it remove the need for manual approvals, middlemen, or third-party verifications. Think automated settlements, royalty distributions, or KYC checks that happen in real time.
A DeFi startup I worked with shaved off weeks of backend ops just by shifting to on-chain logic.
Enhanced Auditability
Blockchain keeps a permanent, timestamped trail of every action. Whether it’s a compliance audit or a supply recall, records are instantly accessible and provable without extra tools needed.
This alone has made many CFOs I’ve worked with raise an eyebrow (in a good way).
Boost in Customer Trust
People are tired of hearing “your data is safe with us.” Blockchain gives you a way to prove it. Transparent smart contracts, verifiable supply chains, or NFT-backed ownership rights all increase credibility in the eyes of tech-savvy users.
And it’s not just small gains we’re talking about.
“Blockchain technology has the potential to boost global gross domestic product (GDP) by US$1.76 trillion over the next decade.”
— PwC
In short, the business case for blockchain is no longer theoretical, it’s becoming a measurable economic driver.
Step-by-Step Guide to Developing a Blockchain Application
Developing a blockchain application isn’t just about writing code, it’s about making strategic technical decisions that directly impact scalability, user trust, and product-market fit. Whether you’re a developer, CTO, or a founder hiring a dev team, this step-by-step breakdown simplifies the complex process.
Step 1 – Define the Problem and Use Case
Before writing a single line of code, ask: Do we actually need blockchain?
Blockchain shines when you need trust without central authority, immutability, or transparency between multiple stakeholders. If a secure shared ledger or automation via smart contracts would improve your product, it’s likely the right choice.
Example:
Instead of a centralized food traceability database owned by one company, use blockchain to create a transparent, tamper-proof record of food origin that all suppliers and buyers can verify.
Step 2 – Choose the Right Blockchain Type
There are three main types:
- Public Blockchains (e.g., Ethereum, Polygon): Fully decentralized and open to anyone. Ideal for DeFi, NFTs, or dApps with global reach.
- Private Blockchains (e.g., Hyperledger Fabric): Controlled by a single organization. Best for internal enterprise use cases like supply chain tracking.
- Consortium/Hybrid Blockchains: Permissioned blockchains governed by multiple entities, good for collaborations between banks, hospitals, etc.
Choose based on your control needs, compliance, and user access model.
Step 3 – Select the Best Blockchain Development Platform
This is where the actual building blocks come in:
- Ethereum: Most widely adopted, mature ecosystem.
- Solana: High-speed transactions, ideal for gaming or trading apps.
- BNB Chain: Lower fees, growing dApp ecosystem.
- Corda: Designed for financial services and regulated industries.
- Hyperledger Fabric: Modular and permissioned — good for enterprise-grade apps.
Your platform choice affects everything from tooling to scalability.
Step 4 – Choose the Consensus Mechanism
(This step is only necessary if you are creating a new blockchain from scratch. If you have already completed step 3, you can skip this.)
This determines how transactions are validated:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Secure but energy-intensive (used in Bitcoin).
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Energy-efficient and faster; now used by Ethereum.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Common in private blockchains; fast but requires pre-approved nodes.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Good for internal systems where validator identity is known.
Pick a mechanism that balances security, speed, and decentralization for your use case.
Step 5 – Design the Architecture
At this stage, you sketch how everything connects:
- Nodes: Where your blockchain data lives and propagates.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing programs that run your logic.
- APIs: For integrating with external apps or third-party services.
- Off-chain Storage: For large files or private data (e.g., using IPFS or AWS).
This blueprint ensures your app is both scalable and secure.
Step 6 – UI/UX Design for Blockchain Apps
Blockchain interfaces often intimidate users. Good design bridges that gap.
Follow Web3 UX principles like clarity, simplicity, and education prompts.
Also, make sure users can connect wallets effortlessly using tools like:
- MetaMask
- WalletConnect
Let users know what permissions they’re granting, especially when signing transactions.
Step 7 – Smart Contract Development
Smart contracts are the logic layer of your app. Choose languages based on your platform:
- Solidity (for Ethereum/BNB Chain)
- Rust (for Solana)
- Go (for Hyperledger or Corda)
Always perform auditing before going live. Tools like MythX, Slither, or hiring a professional audit firm is critical because vulnerabilities in smart contracts are permanent and exploitable.
This related article could be helpful: What is Blockchain Audit: A Comprehensive Guide
Step 8 – Test and Debug Thoroughly
Test across all layers:
- Unit Tests: For smart contract functions
- Integration Tests: End-to-end testing across the dApp stack
- Testnets: Deploy to public testnets like Goerli (Ethereum), Mumbai (Polygon) to simulate real-world conditions.
Catch bugs early – blockchain mistakes are hard (and expensive) to undo.
Step 9 – Deployment and Monitoring
Once testing is complete:
- Use Truffle, Hardhat, or Ganache for streamlined deployment.
- For infrastructure, use Infura or Alchemy to avoid managing your own nodes.
Post-launch, monitor your dApp in real time with tools like:
- Tenderly: Transaction tracing and debugging
- Moralis: Analytics, real-time event tracking, and Web3 backend services
Step 10 – Maintenance, Upgrades, and Governance
Unlike web apps, smart contracts are immutable once deployed, unless you design for upgradability (via proxy patterns).
Also, consider how your app evolves:
- Will changes be voted on via a DAO?
- How do you handle forks or rule changes?
Future-proofing your blockchain app begins on day one.

Blockchain App Tech Stack: Tools and Frameworks
Choosing the right tech stack is critical for building a blockchain app that is scalable, efficient, and developer-friendly. Below are the most reliable tools and frameworks used across the blockchain development lifecycle.
Frontend
To ensure responsive and intuitive user interfaces, developers commonly use:
- React.js: The most popular choice for dApps due to reusable components and a robust ecosystem.
- Vue.js: A lightweight alternative, ideal for projects that value simplicity and quick prototyping.
Both frameworks support seamless integration with Web3 libraries.
Backend
Blockchain apps often use traditional backend logic for off-chain processes, user authentication, and admin control:
- Node.js: Lightweight and event-driven which is perfect for handling multiple wallet connections.
- Go: Offers concurrency and performance, often preferred in blockchain infrastructure tools.
- Python: Known for rapid development and widely used in analytics and scripting for blockchain apps.
Smart Contract Languages
- Solidity: Dominates Ethereum and EVM-compatible chains like Polygon and BNB Chain.
- Vyper: A more secure, readable alternative to Solidity with Python-like syntax, though less mature.
SDKs & Libraries
- Web3.js and Ethers.js: JavaScript libraries that allow interaction with the Ethereum blockchain from your frontend.
- Moralis SDK: Simplifies Web3 backend operations like user login, real-time events, and database sync.
Infrastructure Tools
- IPFS: For storing decentralized files such as NFTs, metadata, and certificates.
- The Graph: Enables fast querying of blockchain data via subgraphs.
- Alchemy: Node-as-a-service that eliminates the need to manage blockchain infrastructure manually.
DevOps & Deployment
- Docker: For containerizing smart contracts and backend services.
GitHub Actions: Automates CI/CD pipelines, including contract deployment and testing.
Cost of Developing a Blockchain Application
Building a blockchain application comes with a wide range of costs that depend on various factors, from the complexity of the features to the blockchain platform and the development model you choose.
Factors That Influence Cost
- Feature Set:
Basic apps (e.g., simple NFT mints) cost far less than complex dApps like decentralized exchanges or DAO platforms. - Chain Selection:
Developing on Ethereum is more expensive due to gas fees and complexity, while Polygon or Solana may lower infrastructure costs. - Smart Contract Scope:
Writing and auditing multiple contracts increases both time and cost. - Team Composition:
Hiring blockchain developers with smart contract expertise adds a premium, especially for Solidity or Rust specialists.
Freelancers vs. Agencies
- Freelancers:
Cost-effective for MVPs or small projects. You can hire a Solidity developer on hourly or per-project terms. - Agencies:
Suitable for larger, regulated apps. They offer full-stack services, from UI/UX to smart contract security audits.
Estimated Budget Range
| Project Scope | Estimated Cost |
| Simple NFT Minting App | $15K – $30K |
| Crypto Wallet or Marketplace | $40K – $75K |
| DeFi Protocol or DAO | $100K – $150K+ |
These rough estimates include design, development, testing, and initial deployment, but not post-launch maintenance.
Ongoing Costs
- Smart Contract Updates (if upgradeable)
- Node access fees (e.g., via Alchemy or Infura)
- Monitoring and security audits
- User support, hosting, and DevOps
Common Challenges and How to Solve Them
Despite its transformative potential, blockchain app development comes with unique technical and operational hurdles. Here’s how to address the most common ones:
1. Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are immutable, meaning any bugs or logic flaws deployed to the blockchain are permanent and potentially costly.
Solution: Always conduct third-party audits, use established libraries like OpenZeppelin, and apply automated tools like MythX or Slither during development.
2. Scalability and Performance
Blockchains like Ethereum struggle with network congestion, high gas fees, and low transaction throughput.
Solution: Use Layer 2 solutions (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism), sidechains (like Polygon), or high-throughput chains like Solana. Off-chain computation via zk-rollups or optimistic rollups also helps.
3. Complex User Experience
Users often find blockchain apps confusing due to wallet connections, gas fees, and complex flows.
Solution: Simplify interfaces, integrate wallet onboarding solutions like Web3Modal, and offer gasless transactions where possible.
4. Regulatory Uncertainty
Laws around crypto, NFTs, and tokens vary widely across jurisdictions and are rapidly evolving.
Solution: Work with legal advisors during ideation. Avoid making unregistered securities or non-compliant tokenomics.
5. Cross-Chain Interoperability
dApps operating on a single chain limit user access and liquidity.
Solution: Design with interoperability in mind using bridges, multi-chain SDKs, or tools like LayerZero and Wormhole.
Best Practices for Secure and Scalable Blockchain Development
Security and scalability should be core design principles from day one, not afterthoughts. The following practices can significantly enhance your blockchain app’s reliability and long-term performance.
1. Use Audited Frameworks and Standards
Avoid reinventing the wheel. Use widely adopted libraries and tools that undergo regular community vetting, like OpenZeppelin for smart contracts and Hardhat or Truffle for deployments.
2. Implement Security Testing at Every Stage
Incorporate tools like:
- MythX: For smart contract vulnerability analysis
- Slither: Static code analysis
- Tenderly: Real-time contract monitoring
Don’t launch before completing both unit and integration testing, especially on Testnets.
3. Follow Modular Code Architecture
Separate business logic from the core smart contracts. This enables easier upgrades, better testability, and higher code reuse. Modular designs also reduce the attack surface.
4. Prepare for Governance Early
If your app involves on-chain governance (like DAOs), plan your governance models and voting mechanisms upfront. Use frameworks like Aragon or Tally to manage proposals and votes securely.
5. Keep Monitoring Post-Launch
Use platforms like Moralis or Tenderly for post-deployment monitoring, contract performance, and on-chain analytics.
Future Trends in Blockchain App Development
Blockchain technology is evolving fast, reshaping the way we build digital products. As developers and startups plan future-ready applications, keeping an eye on the following trends will be critical for staying competitive.
1. Account Abstraction (ERC-4337)
ERC-4337 introduces account abstraction on Ethereum, allowing developers to separate transaction signing logic from the traditional wallet structure. This unlocks features like social logins, gasless transactions, and multi-factor authentication, paving the way for more intuitive dApp user experiences.
2. Zero-Knowledge Technology (zk-Rollups & zkEVM)
zk-Rollups bundle hundreds of transactions into one, verifying them using cryptographic proofs. zkEVMs go a step further, enabling smart contracts on Layer 2 with Ethereum compatibility. This means faster, cheaper, and more secure execution without compromising decentralization.
3. AI-Integrated Smart Contracts
The intersection of AI and blockchain is beginning to take shape. Developers are exploring smart contracts that respond to AI-generated insights — automating decisions in DeFi, dynamic NFTs, and predictive DAO governance. Expect greater experimentation in this space.
4. Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
With Ethereum’s mainnet often congested, Layer 2 solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum, and Base continue gaining traction. These networks drastically reduce gas costs and speed up transaction finality, enabling better UX without leaving the Ethereum ecosystem.
5. Cross-Chain Interoperability
The future is multi-chain. Protocols like Cosmos IBC, Polkadot, and Chainlink CCIP are making it easier for apps to communicate across blockchains – allowing users and developers to move assets, data, and logic fluidly across ecosystems.
6. Blockchain in IoT and Smart Cities
As physical infrastructure integrates with digital systems, blockchain becomes essential for secure, decentralized data sharing.
“The Global Blockchain IoT Market size is expected to reach $11.9 billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 57.2% CAGR during the forecast period.”
— KBV Research
Conclusion
Blockchain application development is no longer a niche experiment, it’s a foundational shift in how digital systems operate. From transparent finance solutions and secure healthcare systems to tokenized real estate and cross-border supply chains, blockchain is reshaping how businesses think about trust, data, and automation.
This guide has walked you through the entire development lifecycle, from defining your use case and choosing the right blockchain architecture, to designing, building, and scaling your application. You’ve also seen how real-world companies are already leveraging blockchain across industries, and where the technology is headed next.
If you’re a developer, product owner, startup, or enterprise exploring this space, now’s the time to act. Whether you want to prototype a minimal version, consult with blockchain experts, or simply deepen your understanding with the tools, communities, and resources are more accessible than ever.
The blockchain landscape is still unfolding. New protocols, tools, and standards are emerging almost monthly. Staying curious, adaptive, and informed will be the key to building something that not only works; but lasts.
Here are some FAQs we encounter by several of our readers
What are the main types of blockchain networks?
There are four main types:
- Public blockchains (e.g., Ethereum, Bitcoin): Open to anyone and maintained by decentralized participants.
- Private blockchains (e.g., Hyperledger Fabric): Controlled by a single organization, used for internal use cases.
- Consortium blockchains (e.g., Corda): Controlled by a group of organizations with shared governance.
- Hybrid blockchains: Combine features of both public and private networks, offering flexible control and transparency.
Choosing the right type depends on your business model, security needs, and user base.
How long does it take to develop a blockchain app?
Development time can vary based on complexity and team size:
- Simple MVP (wallet, basic contract): 3–6 weeks
- Moderate complexity (DeFi app, NFT marketplace): 2–3 months
- Enterprise-grade app with custom integrations: 4–6+ months
Testing, auditing, and compliance steps can extend timelines but are essential for launch-readiness.
Can I use traditional programming languages for blockchain apps?
Yes, especially for frontend and backend development:
- Frontend: JavaScript, TypeScript (React, Vue)
Backend: Node.js, Python, Go
However, smart contract development requires blockchain-native languages like Solidity, Rust, or Vyper depending on the chain (e.g., Ethereum, Solana).
What are the top platforms for launching a dApp?
Popular choices include:
- Ethereum – most widely used and supported
- BNB Chain – faster and more affordable gas fees
- Polygon – Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum
- Solana – high-speed performance
- Corda & Hyperledger – preferred for enterprise use cases
Platform selection should be based on your app’s audience, performance needs, and dev ecosystem.c
How do I ensure smart contract security?
Best practices include:
- Writing modular and minimal contracts
- Using audited libraries (e.g., OpenZeppelin)
- Performing tests with tools like Slither, MythX, and Hardhat
- Conducting formal security audits before deployment
Planning for upgradability via proxy contracts or governance models
What is gas optimization and why is it important?
Gas refers to the fee users pay to execute transactions on blockchains like Ethereum. Poorly optimized contracts can result in:
- Higher costs for users
- Slower execution
- Network congestion
Gas optimization reduces operational costs and enhances the UX. Techniques include minimizing storage writes, reusing variables, and streamlining logic.
Partner with Us
If you’re looking to build a secure, scalable, and future-ready blockchain solution — we can help. Whether it’s a proof of concept (POC) workshop, a smart contract audit, or end-to-end development, our team at Webisoft is equipped with both the technical depth and practical experience to guide you.
📌 Start with a consultation. Build smart. Build with confidence.
